How to Cure Acne: A Comprehensive Guide to Clearer Skin
Acne is a common skin condition affecting people of all ages, from teenagers to adults. It can range from mild breakouts to severe cystic acne that can lead to scarring and emotional distress. While there’s no one-size-fits-all cure for acne, effective treatments and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce its impact. This comprehensive guide explores the causes of acne, types of acne, medical treatments, and natural remedies to help you achieve clearer skin.
Understanding Acne
Acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, leading to inflammation. To effectively manage acne, it’s crucial to understand its underlying causes:
- Excess Sebum Production: Sebaceous glands produce oil (sebum) that, when overproduced, can clog hair follicles.
- Bacterial Growth: Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes) is a bacterium commonly found on the skin. When it accumulates, it can lead to inflammation and acne.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy, can trigger acne.
- Genetics: A family history of acne increases your likelihood of developing it.
Types of Acne
Acne can manifest in different forms, each requiring a unique approach to treatment:
- Blackheads: Open comedones where sebum oxidizes, creating dark spots.
- Whiteheads: Closed comedones with a white or flesh-colored appearance.
- Papules: Small, red, inflamed bumps without pus.
- Pustules: Similar to papules but contain pus, leading to a white or yellow head.
- Nodules: Larger, painful lumps deep within the skin.
- Cysts: Severe, pus-filled lesions that can cause scarring.
Medical Treatments for Acne
Medical treatments are often the most effective way to manage acne. Here’s an overview of the commonly used treatments:
Over-the-Counter Treatments
These treatments are readily available and can be effective for mild to moderate acne:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This ingredient kills bacteria and reduces oil production. It is available in various forms, including cleansers, gels, and creams.
- Salicylic Acid: A beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) that helps exfoliate dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Alpha-Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): These acids, such as glycolic acid, promote cell turnover and can help reduce acne scars.
- Sulfur: Known for its antibacterial properties, sulfur can dry out excess oil and reduce inflammation.
Prescription Medications
For moderate to severe acne, you may need prescription medications from a dermatologist:
- Topical Retinoids: Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, help unclog pores and promote skin renewal. Tretinoin and adapalene are common examples.
- Topical Antibiotics: These reduce bacteria and inflammation. They are often combined with benzoyl peroxide to prevent antibiotic resistance.
- Oral Antibiotics: Prescribed for more severe acne to combat bacteria and reduce inflammation from the inside out.
- Hormonal Treatments: Birth control pills or anti-androgen medications can help balance hormones that contribute to acne in women.
- Isotretinoin: A powerful oral retinoid used for severe cystic acne. It requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects.
Professional Treatments
Dermatologists offer specialized treatments to manage acne and its complications:
- Chemical Peels: These involve applying a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin and unclog pores.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments target bacteria and reduce oil production.
- Extraction: A dermatologist manually removes blackheads and whiteheads to clear clogged pores.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Used for large, inflamed nodules or cysts to reduce pain and swelling.
Natural Remedies for Acne
In addition to medical treatments, natural remedies can play a role in managing acne. Here are some popular natural approaches:
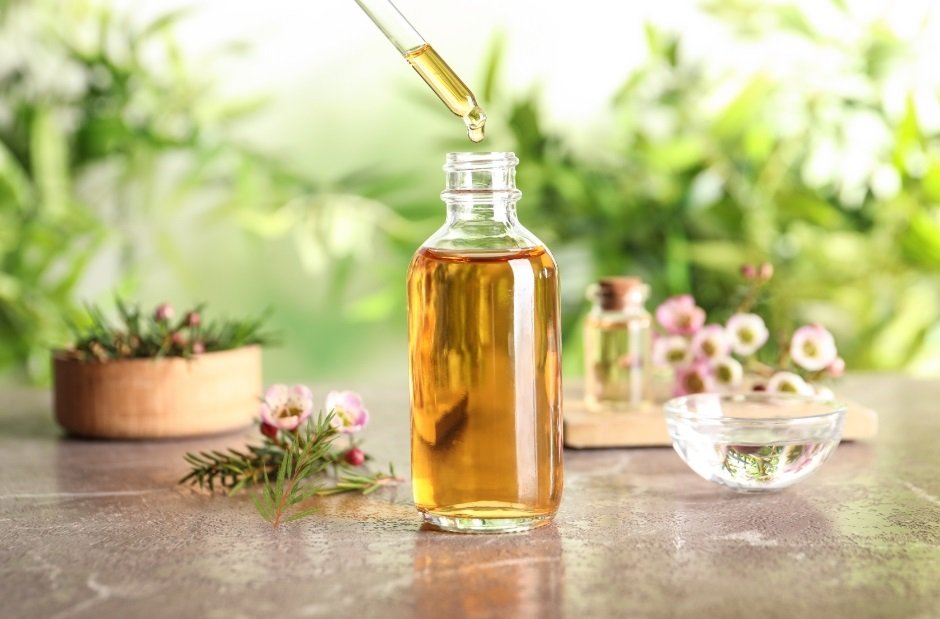
1. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a popular choice for treating acne.
How to Use It: Dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil (like jojoba or coconut oil) at a ratio of 1:10. Apply the diluted oil to affected areas with a cotton swab. Do not use undiluted tea tree oil on the skin, as it can cause irritation.

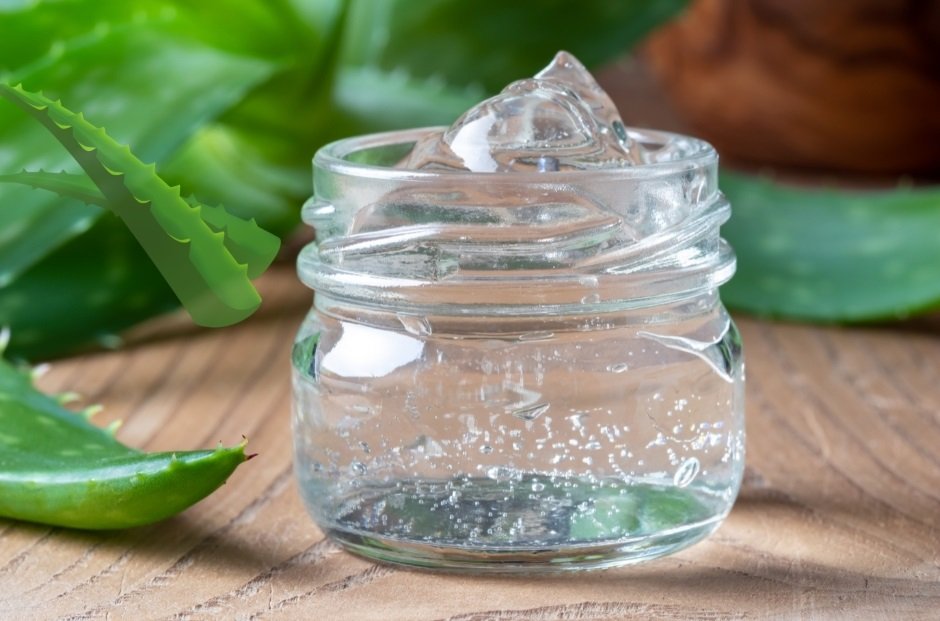
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory effects, making it beneficial for reducing acne redness.
How to Use It: Apply pure aloe vera gel to the affected areas twice a day. You can use aloe vera gel from the plant or purchase pure aloe vera products.

3. Green Tea
Green tea contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, making it useful for acne treatment.
How to Use It: Brew green tea and let it cool. Apply the cooled tea to your face with a cotton ball or spray bottle. You can also drink green tea regularly to reduce inflammation from within.

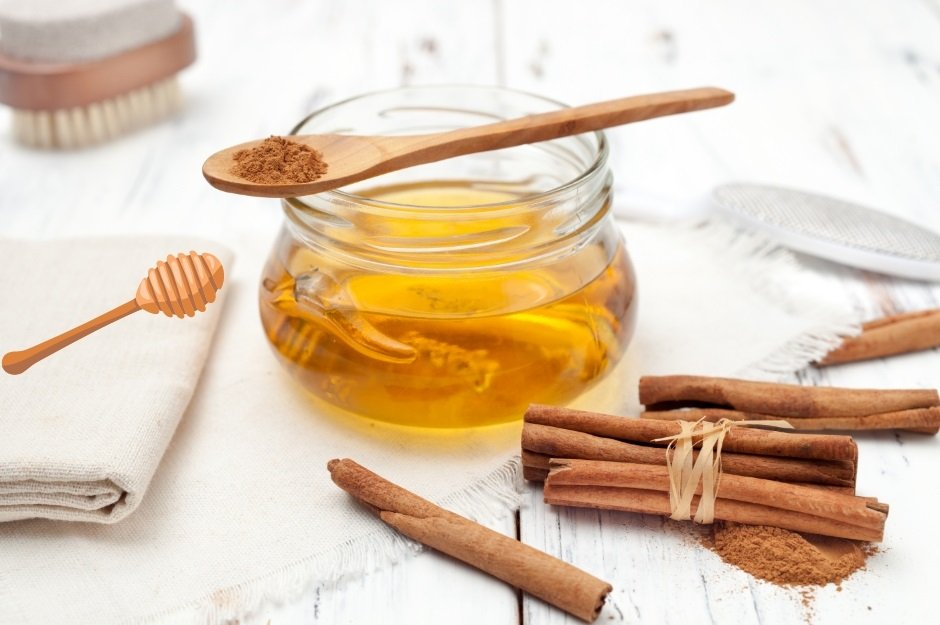
4. Honey and Cinnamon Mask
Honey has antibacterial properties, and cinnamon has anti-inflammatory effects, making this combination an effective mask for acne.
How to Use It: Mix 1 tablespoon of honey with 1 teaspoon of ground cinnamon. Apply the paste to your face and leave it on for 10-15 minutes. Rinse off with warm water and pat dry.

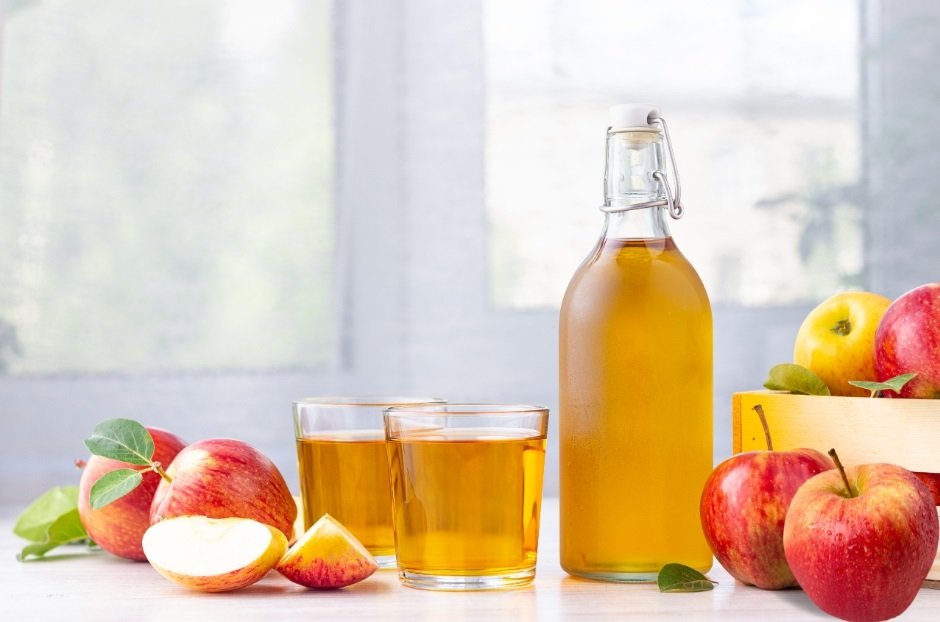
5. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar contains organic acids that can help exfoliate the skin and reduce bacteria.
How to Use It: Dilute apple cider vinegar with water at a ratio of 1:3 or 1:4. Apply the diluted mixture to your face using a cotton ball. Let it sit for a few minutes before rinsing off with water. Be cautious, as apple cider vinegar can irritate sensitive skin.

Lifestyle Changes to Manage Acne
Besides medical and natural remedies, lifestyle changes can significantly impact acne management. Here are some tips for a healthier lifestyle that can help reduce acne:
- Establish a Gentle Skincare Routine: Use non-comedogenic products and avoid harsh scrubs or aggressive cleansing. Stick to a simple skincare routine that includes cleansing, moisturizing, and sun protection.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Consuming foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, and avoiding high-glycemic foods and excessive dairy can help manage acne.
- Manage Stress: Stress can worsen acne. Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing to manage stress levels.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain healthy skin and supports overall health.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support skin repair and rejuvenation.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
If over-the-counter treatments, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes don’t lead to significant improvement, it’s best to consult a dermatologist. A dermatologist can provide personalized advice and recommend advanced treatments to manage acne effectively.
SUMMARY
Acne is a complex condition with a variety of contributing factors, from hormonal changes and bacterial growth to genetics. While there is no universal cure, a combination of medical treatments, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes can lead to clearer skin. Whether you’re using benzoyl peroxide, tea tree oil, or adjusting your diet, remember that patience and consistency are key to seeing results. If you’re struggling with severe acne or complications, seek professional help to create a personalized treatment plan. With the right approach, you can achieve healthier, clearer skin.












